The Anatomy of a Protected LiIon Battery
A protected battery will (hopefully) include the following protections:
- PTC, protect against over temperature and indirectly over current and will automatic reset.
- CID or pressure valve, will disable the cell permanently if the pressure is to high in the cell (Can be due to over charge).
- PCB will protect against over discharge, over charge and over current, depending on design the PCB will reset automatic or when placed in a charger.
Unprotected batteries are missing the PCB protection, but usual has the PTC and CID. The PCB protection is highly recommended for some LiIon batteries (LiCoO2). Here I am going to show how this PCB is fitted into a LiIon battery.

The above drawing illustrates how a protected cell is build. This construction is used for any type of protected LiIon battery, I have dissected a AW 18650 battery and a Soshine battery to see the extra protection. The PTC and pressure valve will not be visible, because it is part of the original battery, but all the other parts of the protection can be seen.
If the pressure valve opens the connection between the internal plus pole and the external plus pole on the battery will be broken. For this reason it is also called a CID for current interrupt device.


The battery is a 18650 battery, with this name it is supposed to be 18 mm in diameter and 65 mm long. These measurements do not fit reality completely, the battery is a few mm longer and has a bit larger diameter, due to the added protection..

The holes in the plus pole of the battery is the exhaust from the pressure valve in the battery, this can be seen on many types of batteries. Also hidden beneath the plus is a temperature fuse (Called a PTC resistor), but it cannot be seen here. For batteries with the optional top, the holes will also be present in that.
Note: This protection is enough for some manufacturer to call a battery protected, but a phrase like "pcb protection" or "IC protection" does cover a battery with full protection.




Note the narrowing on the backend of the battery and it also looks like there is something on the side of the battery. Both are signs that this battery has a electronic circuit in the back and usual this circuit is the extended protection. For standalone LiIon batteries (LiCoO2) it is very important that this protection is present. In packs with multiple cells this circuit is usual common for the pack and not mounted in each cell.
A battery with a copper bottom and maybe some letters etched into the copper is also a sure sign of a protected battery, but it also implies that the battery is missing the extra metal plate to make a strong bottom.
Note: Cell is a battery with only one "battery" in it, battery is a collection of cells but also used about a single cell (Does this sentence make sense?).



In thees picture I have removed the wrapper around the battery and the circuit at the bottom of the battery can be seen, together with the wire on the side of the battery.



The wire is connected to the plus pole on the battery and the other end goes to the circuit in the bottom of the battery. The vent holes, from the pressure valve, can also easily be seen here, including two more.


On this cell the plus pole was pushed out of adjustment, this is because it is an optional button top that has been mounted on the cell.
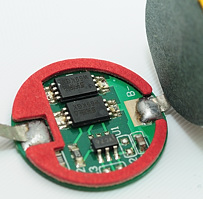
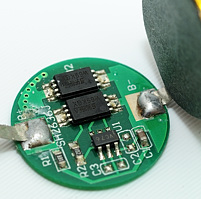

The wire is soldered to the circuit at the bottom and another wire goes from the circuit to the bottom of the battery, i.e. the (internal) minus pole. The (external) minus pole of the battery is the backside of the circuit, not the minus pole on the cell. There is some protective paper on the minus pole of the cell.

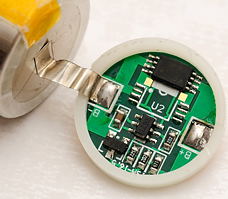
The Soshine battery uses a plastic spacer and some protective paper on top of the circuit.

In this picture I have collected all the parts from the battery, the actual 18650 cell in a metal shell, the protection circuit that is mounted at the minus pole of the cell and various isolation pieces and spacers, together with the black wrapper that is placed around everything.
Measuring the cell, without wrapper, wire and circuit, it is exactly 18 mm in diameter and only 64.7 mm long, i.e. the 18650 specification fits.
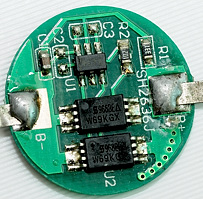


One these pictures I show some different protection circuits, the last one is for a smaller battery (The scale is different, I have zoomed close on the last picture, all parts looks bigger).
This cirucit usual protect against over discharge, over charge, and to high current drain (Short circuit).

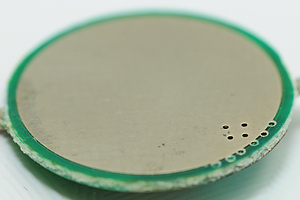
The protection circuit seen from the backside, i.e. the actual/external minus pole on the protected battery. As can be seen, one of the circuits has an extra metal plate on the back of the circuit, to make the minus pole more durable.



The circuit has two important elements, the blue circle is around the controller chip and the red circle is around the switch that is used to connect/disconnect the battery.
Measuring on the protection circuits I found:
AW:
Current consumption: 4.5 uA, i.e. it will discharge a 2000mAh battery in 50 years
Overdischarge will disconnect at 2.5 volt, but will only reconnect if the battery goes above 3 volt.
Overcharge will disconnect at 4.26 volt and will reconnect when battery is removed from charger.
Voltage drop in circuit at 1 amp and 2.9 volt battery voltage: 25mV
The other big circuit:
Current consumption: 4.2 uA
Overdischarge will disconnect at 2.5 volt, but will not reconnect again except with external voltage (i.e. a charger).
Overcharge will disconnect at 4.26 volt and will reconnect when battery is removed from charger.
Voltage drop in circuit at 1 amp and 2.9 volt battery voltage: 30mV
The small circuit:
Current consumption: 3.9 uA
Overdischarge will disconnect at 2.5 volt, but will not reconnect again except with external voltage (i.e. a charger).
Overcharge will disconnect at 4.26 volt and will reconnect when battery is removed from charger.
Voltage drop in circuit at 1 amp and 2.9 volt battery voltage: 60mV
The above measurements are only valid for the circuits I have measured on, but gives an indication about what to expect from LiIon protection circuits.
Notes
How to see if a battery is protected
Comparison and test of 18650 batteries and similar sizes, both protected and unprotected
Comparison and test of 14500/16350 batteries and other small sizes, both protected and unprotected
Comparison and test of 26650 batteries and similar sizes, both protected and unprotected





























